What is the height of a dock door?
A standard dock door height typically ranges from 8 to 14 feet, depending on operational needs.
Standard Dock Door Dimensions
Common height and width measurements
Dock doors, essential components in warehouses and distribution centers, come in standardized measurements to accommodate the vast majority of vehicles and freight. Generally:
- Height: The typical height for dock doors in many warehouses ranges between 8 to 10 feet. However, there are taller dock doors designed specifically for larger vehicles, and these can measure up to 12 to 13 feet.
- Width: A standard dock door width tends to be approximately 8 to 10 feet wide. This width allows easy access for most trucks and trailers while providing some leeway for loading and unloading.
It’s worth noting that these are general standards, and custom sizes might be necessary depending on specific requirements.

Factors influencing standard dimensions
Several factors dictate the dimensions of a dock door, ensuring that they suit the operational needs of a facility:
- Vehicle Sizes: Different vehicles, whether they’re vans, standard trailers, or oversized trucks, have varying heights and widths. Dock doors must accommodate the most common vehicles that will be accessing the facility.
- Freight Dimensions: The size and nature of the goods being loaded or unloaded can influence dock door dimensions. For instance, facilities handling large machinery might require taller and wider doors.
- Operational Efficiency: A door that’s too small can slow down operations, while an excessively large door might lead to energy inefficiencies, especially in temperature-controlled environments.
- Future Proofing: As industries evolve and equipment changes, warehouses might opt for slightly larger dimensions to ensure they’re ready for future requirements.
Cost Implications: The price of a dock door primarily depends on its material, insulation properties, and dimensions. On average, a standard sized dock door can range between $1,000 to $4,000. Customized sizes and features can push this price higher. It’s crucial to factor in installation costs, potential energy savings, and long-term durability when considering the total cost.
Types of Dock Doors
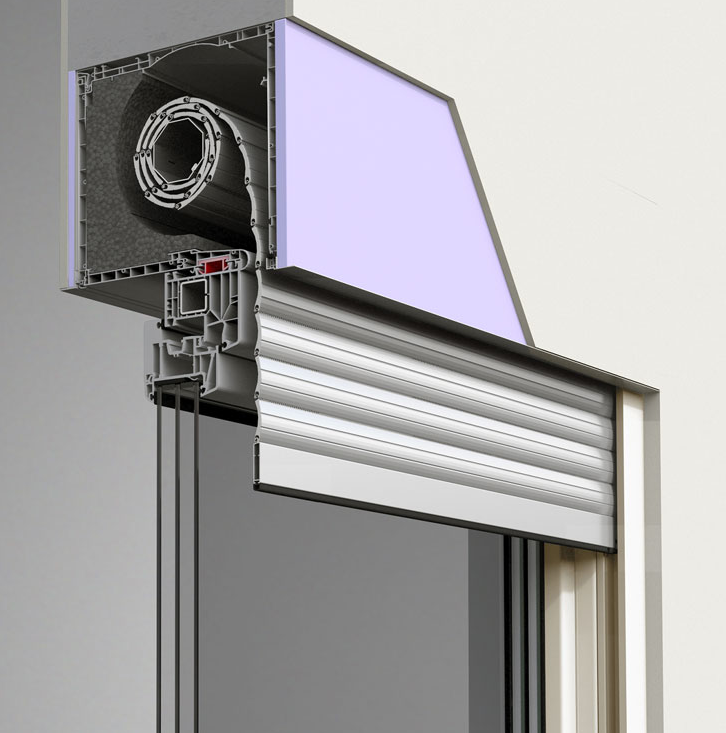
Roll-up doors
Roll-up doors, as the name suggests, roll up into a coil when opened. They often consist of horizontal slats that allow them to be rolled up tightly and use minimal overhead space. Roll-up doors can be manual or motor-operated, depending on the size and frequency of operation. These doors are popular due to their space-saving design and can be commonly found in urban warehouses where space is at a premium. For added security and durability, some facilities opt for steel roll-up doors.
Sectional overhead doors
Sectional overhead doors are made up of panel sections that are connected with hinges. As the door opens, wheels at the edge of each panel roll inside a vertical track on each side of the door opening. The hinges between each panel section bend over a curved portion of the track, which leads the door to sit parallel with the ceiling when fully open, or perpendicular when completely closed. They are often used in environments where temperature control is critical, thanks to their tight seal and insulating properties.
Sliding doors
Sliding doors typically operate by sliding horizontally on a track, parallel to the wall. They are ideal for wide openings and are commonly used in large warehouses. One of their key advantages is that they do not require any overhead space, unlike roll-up or sectional doors. However, they do need sufficient wall space on one or both sides of the door opening to accommodate the door’s full width when it’s open.
Vertical lift doors
Vertical lift doors rise straight up and remain inside the building, without rolling or sliding to the side. They’re especially useful in areas where side room or headroom is limited and are often used for large equipment or aircraft hangars. Given their vertical movement, these doors can accommodate taller vehicles and machinery without requiring extra width.
Determining Appropriate Dock Door Height
Truck heights and variations
Choosing the right dock door height must account for the various trucks that will be accessing the facility. There’s a considerable difference in height between smaller delivery vans, standard shipping trucks, and oversized trailers. For instance:
- Delivery vans: Typically 8 to 9 feet in height.
- Standard shipping trucks: Often range between 12 to 13.5 feet, with some variations.
- Oversized trailers: Can reach up to 14 feet or even more.
To accommodate a broad range of vehicles, many facilities opt for dock doors that can comfortably fit the tallest trucks they anticipate servicing. But it’s also crucial to consider the local regulations and road transport standards as truck heights can vary by region and country.
Cargo dimensions and loading methods
The height of the goods being transported is another vital factor. If a facility primarily deals with large machinery or tall stacked pallets, then a taller dock door is essential. It’s not just about the cargo height, but also the equipment used for loading and unloading, such as forklifts with tall masts or specialized cranes. The door height should allow for both the cargo and the equipment to move in and out without obstructions.
Facility design and constraints
Every facility comes with its unique architectural constraints and operational requirements. Some older buildings might have lower ceiling heights or structural beams that limit the height of dock doors. In contrast, modern warehouses designed for high-throughput logistics might prioritize taller and wider doors. Furthermore, the dock’s design, whether it’s a flush dock or an enclosed dock, can also influence the height of the door.
Cost Implications: Door height can influence the cost, with taller custom doors typically being more expensive. A standard 10-foot tall door might range from $1,500 to $3,500, while a taller 14-foot door could be upwards of $4,500 or more. However, the long-term operational benefits of selecting the right door height can often outweigh the initial cost difference.
Impact of Inappropriate Dock Door Height
Challenges in loading and unloading
Having a dock door that’s not the right height can lead to numerous complications during the loading and unloading process. For starters, if the door is too short, taller vehicles might not be able to access the dock, leading to delays as alternative loading areas or methods are sought. Additionally, tall cargo items or loading equipment, like forklifts with extended masts, might face obstructions, requiring manual handling or time-consuming workarounds. In a fast-paced logistics environment, these inefficiencies can lead to significant bottlenecks and delayed shipments.
Potential damages to goods and infrastructure
A mismatch in dock door height can risk both the goods being transported and the infrastructure itself. For example, a truck trying to fit into a shorter dock can lead to roof or structural damages to the vehicle. Similarly, cargo being forcefully passed through a shorter door might sustain damages, impacting the integrity of the goods and leading to financial losses. There’s also the risk of damage to the dock door mechanisms if trucks collide with the structure, leading to repair costs and operational downtimes.

Implications on safety and operations efficiency
Safety should always be a top priority in warehousing and logistics. An inappropriate dock door height can introduce various safety risks. Employees trying to manually maneuver cargo through a door that’s too short or using equipment inappropriately can face injury risks. Additionally, vehicles trying to access docks not suited to their size can lead to accidents, potentially injuring drivers and ground staff. From an operational efficiency standpoint, the wrong door height can lead to longer loading times, increased labor costs, and a slower overall turnaround, impacting the facility’s throughput and profitability.
Adjusting and Retrofitting Existing Dock Doors
Techniques to increase door height
Adjusting an existing dock door’s height can be a complex process but is often necessary to meet evolving operational needs. Some common methods include:
- Relocation of Header: Raising the header or the structural frame at the top of the door can provide additional height. This often requires reinforcing the surrounding structure to ensure stability.
- Extending Door Tracks: Lengthening the tracks that guide roll-up or sectional doors can allow them to open higher, providing greater clearance.
- Replacing with Taller Doors: In some cases, it might be simpler to replace the entire door with a taller model. While more drastic, it ensures the new door fits seamlessly into the operational workflow.
- Use of Flexible Curtains: Switching to flexible curtain doors can provide added height flexibility, as these doors can fit into various openings and are adjustable to different heights.
Benefits and limitations of retrofitting
Benefits:
- Operational Flexibility: Retrofitting doors allows warehouses to accommodate a wider range of vehicles and cargo, increasing versatility.
- Increased Efficiency: By minimizing the challenges faced due to incorrect door height, operations can run smoother and faster.
- Cost Savings: Over time, retrofitting can lead to savings by reducing cargo damage, improving energy efficiency (if doors are better insulated), and decreasing manual labor.
Limitations:
- Structural Challenges: Not all warehouse structures can easily accommodate changes to dock door height. There might be structural or foundational constraints.
- Downtime: The retrofitting process can lead to operational downtime, which needs to be factored into the decision.
- Temporary Solutions: Some retrofitting solutions might serve as a patch rather than a long-term solution, requiring future adjustments.
Cost implications
The cost of retrofitting a dock door varies based on the complexity of the project and the specific technique used. Here’s a rough breakdown:
- Relocating the Header: This can be one of the more expensive options, with costs ranging from $5,000 to $10,000, depending on structural complications.
- Extending Door Tracks: A relatively affordable method, extending tracks can cost between $1,000 to $3,000, depending on the door type and length of extension.
- Replacing with Taller Doors: The cost here depends on the door model chosen, but on average, it can range from $2,500 to $6,000.
- Flexible Curtain Doors: The price varies based on size and features, but typically ranges from $3,000 to $7,000.
Additional costs can arise from labor, potential structural assessments, and any other facility adjustments needed to accommodate the new door height.