Both PVC and Aluminium doors have pros and cons in terms of cost, durability, and environmental impact. Your choice should align with your specific needs and priorities.
Materials Overview
When choosing a door for your home or commercial space, the material plays a pivotal role in determining the performance, durability, and aesthetic appeal of the door. Two popular materials in today’s market are PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) and Aluminium. This section aims to provide an in-depth look at the properties of each material to better inform your decision-making process.
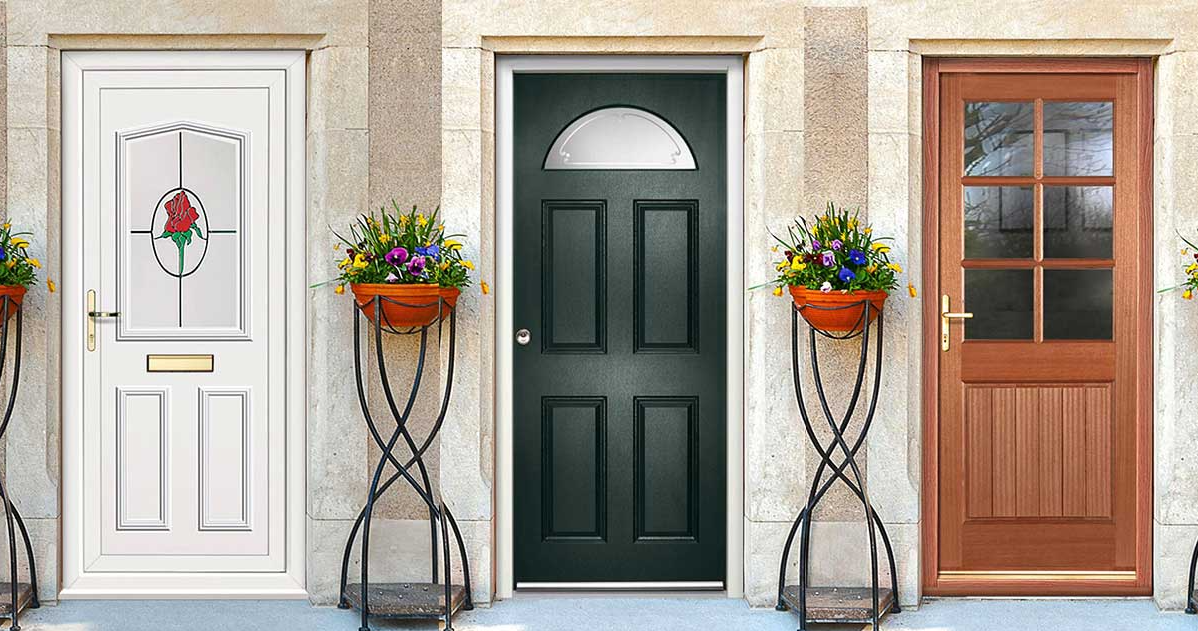

Properties of PVC
PVC, or Polyvinyl Chloride, is a type of plastic polymer widely used in construction. It is most commonly employed in window and door frames, as well as in plumbing and electrical insulation.
- Cost-Effective: PVC is generally cheaper than other materials, such as aluminium or wood.
- Insulation: PVC offers excellent thermal and sound insulation properties.
- Low Maintenance: Requires very little upkeep—typically, a wipe down with soapy water is sufficient.
- Color Options: Comes in a variety of colors and finishes, including wood-like textures.
- Durability: Although not as strong as aluminium, PVC is still fairly durable and can last up to 25 years with proper care.
- Chemical Resistance: Resistant to most acids, bases, and salts, making it less susceptible to corrosion.
For more information, you can visit PVC Wikipedia.
Properties of Aluminium
Aluminium is a light-weight, high-strength metal often used in door frames and other construction applications. It is also widely used in the aerospace and automotive industries.
- Strength: Aluminium is significantly stronger than PVC, able to withstand heavy impacts without deforming.
- Aesthetic Flexibility: Available in an array of finishes and can easily be painted or anodized.
- High Thermal Conductivity: Without thermal breaks, aluminium is a poorer insulator than PVC.
- Longevity: When properly maintained, aluminium doors can last for 40 years or more.
- Recyclability: Aluminium is 100% recyclable, which has environmental benefits.
- Cost: Generally, aluminium is more expensive than PVC, both in initial costs and long-term maintenance.
For a detailed understanding, visit the Aluminium Wikipedia page.
Cost Analysis
One of the most critical factors in choosing a door material is cost. Both initial and long-term expenditures can significantly impact your decision. Below, we break down the various cost aspects associated with PVC and Aluminium doors to give you a comprehensive understanding of where your money goes.
Initial Costs
When it comes to initial outlay, PVC doors generally come out ahead in terms of affordability.
- PVC: You can expect to pay between $200 to $600 for a basic PVC door. Customizations and designer features will add to this base cost.
- Aluminium: The starting range for aluminium doors is typically higher, around $400 to $1,200 for standard models. High-end versions can go up even more, especially if you’re looking for specialized finishes or robust security features.
You can visit Cost Analysis Wikipedia for more insights on how cost analysis is conducted.
Long-term Costs
While initial costs are crucial, it’s also important to consider long-term expenses, such as durability and maintenance, which we will detail in the next section.
- PVC: Though cheaper initially, PVC doors may require replacement sooner than aluminium doors. However, they offer excellent insulation, which could save you on energy bills.
- Aluminium: Despite the higher upfront cost, aluminium doors generally last longer and could prove to be cost-effective in the long run. Yet, they might contribute to higher energy costs due to their poor insulation properties without thermal breaks.
You can further explore this on the Life-Cycle Cost Wikipedia page.
Maintenance Costs
Maintenance costs can also add up over the years, affecting the total cost of ownership.
- PVC: Very low maintenance, usually just requiring a wipe down with a damp cloth. There’s no need for repainting or resealing, which keeps long-term maintenance costs low.
- Aluminium: While robust, aluminium may require periodic treatment to prevent corrosion, especially in salty or humid environments. Repainting or anodizing may be needed over time, adding to the total cost.
For a better understanding of maintenance economics, you may refer to Maintenance Wikipedia.
Durability and Longevity
When investing in doors for a home or business, durability and longevity stand out as top considerations. A door is not just an entry point but also a barrier against external factors, from weather to potential security threats. Hence, understanding the lifespan and resilience of PVC and Aluminium doors can play a crucial role in making a wise purchase decision.
Lifespan of PVC Doors
PVC doors have been a popular choice for their affordability and decent durability.
- Average Lifespan: A PVC door typically lasts between 20 to 25 years with proper care.
- Weather Resistance: PVC is resilient against rain and does not rot or rust. However, prolonged exposure to sunlight might cause it to become brittle or discolored.
- Impact Resistance: While sturdy, PVC doors can be susceptible to heavy impacts and might crack or warp over time.
- Maintenance Impact: Given their low maintenance requirements, a well-maintained PVC door can serve reliably for years.
For a comprehensive understanding of the material, refer to Polyvinyl Chloride Wikipedia.
Lifespan of Aluminium Doors
Aluminium, renowned for its strength and lightness, offers a different set of advantages.
- Average Lifespan: Aluminium doors can last upwards of 30 to 40 years, making them a durable choice.
- Weather Resistance: Aluminium is corrosion-resistant, especially when anodized or coated. This makes it ideal for humid or coastal areas.
- Impact Resistance: Thanks to its inherent strength, aluminium doors excel in withstanding impacts, making them ideal for high-traffic areas or places prone to rough use.
- Maintenance Impact: With occasional maintenance to prevent corrosion or wear, aluminium doors can remain functional and aesthetically pleasing for decades.
For a detailed dive into the properties of aluminium, visit Aluminium Wikipedia.
Thermal Efficiency
Energy efficiency is an ever-growing concern for both homeowners and commercial property managers. Thermal efficiency, in particular, has a direct impact on heating and cooling costs, as well as the overall comfort level inside a building. Let’s examine how PVC and Aluminium doors perform in this vital area.
PVC and Insulation
PVC is well-known for its excellent insulation properties, making it a go-to choice for those looking to maximize thermal efficiency.
- Heat Retention: PVC doors are excellent at retaining heat during colder months, contributing to a warm and cozy indoor environment.
- Cooling Efficiency: During hot seasons, PVC acts as a good barrier, keeping the inside of the home cooler than external temperatures.
- Energy Savings: Thanks to its insulating properties, PVC can help you save on energy bills, particularly for heating and cooling.
- Weather Seals: Many PVC doors come with built-in weather seals that further enhance their insulating properties.
For an in-depth understanding, refer to the Thermal Insulation Wikipedia page.
Aluminium and Insulation
Aluminium, despite its many advantages, falls short when it comes to natural insulation capabilities.
- Thermal Breaks: Newer aluminium doors come with “thermal breaks,” layers of insulating material inserted between the interior and exterior layers of the door to improve insulation.
- Dual-Pane Glass: Aluminium doors often use dual-pane or even triple-pane glass to offset the metal’s lack of insulating properties.
- Conductivity: Aluminium is a good conductor of heat, meaning that without these additional measures, it can make for a poor insulator.
- Energy Efficiency: Because of these factors, aluminium doors without added insulation features can contribute to higher energy costs for heating or cooling.
More about the thermal properties of materials can be found on the Thermal Conductivity Wikipedia page.
Aesthetic Appeal
The aesthetic appeal of a door is not just a vanity point but also an element that adds value to your property. A well-designed door can complement your home’s architecture, create a strong first impression, and even influence natural lighting. In this section, we explore the design flexibility of both PVC and Aluminium doors to help you decide which aligns best with your aesthetic requirements.
Design Flexibility of PVC
PVC doors come in a broad range of styles, colors, and finishes, making them a versatile choice for various architectural styles.
- Color Variations: PVC doors are available in multiple colors, and some even mimic natural wood finishes.
- Textures: Whether you prefer a smooth or wood-grain texture, PVC offers plenty of options.
- Glass Inserts: Many PVC doors come with customizable glass inserts, allowing you to add an extra design element.
- Hardware Compatibility: PVC doors work well with a variety of hardware styles, be it modern or traditional.
For more ideas on interior design and aesthetics, you can visit the Interior Design Wikipedia page.
Design Flexibility of Aluminium
Aluminium doors offer an entirely different set of aesthetic opportunities, particularly appreciated in modern architectural settings.
- Sleek Designs: Aluminium doors can be designed with slim frames and large glass panels, ideal for modern, minimalist homes.
- Finish Options: From matte to shiny, anodized to powder-coated, the finish options for aluminium are numerous.
- Custom Shapes: Aluminium’s strength allows for custom shapes and expansive sizes, facilitating creative architectural designs.
- Color Matching: While not as diverse as PVC, aluminium still offers a good range of color options, especially through anodizing or painting.
To delve deeper into architectural styles, consider exploring the Architectural Design Wikipedia page.
Security Features
Security is a paramount concern for anyone installing a new door. A door serves as a vital entry point, and it needs to be as secure as possible to protect against unauthorized access. We’ll examine the various security features available for both PVC and Aluminium doors to help you make an informed decision.

Locking Mechanisms for PVC
PVC doors usually come with a range of locking options, but their overall strength is also influenced by the material itself.
- Multi-Point Locking: PVC doors commonly feature multi-point locking systems that secure the door at various points along the frame.
- Keyless Entry: Modern PVC doors also offer keyless entry systems, such as digital keypads and even smart lock compatibility.
- Reinforcement: Some PVC doors have steel or metal reinforcement inside the frames to add rigidity and improve security.
- Glazing Options: Double or triple glazing can also make it more difficult for intruders to break the glass and gain entry.
To get more information about various types of locks and their history, you can visit Lock (security device) Wikipedia page.
Locking Mechanisms for Aluminium
Aluminium doors are inherently stronger than PVC, giving them an edge in security right off the bat.
- High-Security Locks: Aluminium doors can be fitted with high-security mortise locks that are challenging to tamper with.
- Biometric Systems: Due to their sturdy construction, aluminium doors are often compatible with advanced security features like biometric systems.
- Impact Resistance: The robust nature of aluminium itself provides an extra layer of security, resisting forced entries more effectively.
- Security Screens: Aluminium doors can be combined with security screens for an added layer of protection, making them almost impenetrable.
For more details on home security, check out the Home Security Wikipedia page.
Environmental Impact
As global awareness of environmental issues grows, the sustainability of building materials is an increasingly important factor in decision-making. The environmental impact of your door choice involves not just its long-term use but also its production and disposal processes. Below, we’ll explore the sustainability aspects of PVC and Aluminium doors.
Sustainability of PVC
PVC is a mixed bag when it comes to environmental sustainability.
- Resource Intensity: PVC manufacturing involves the use of petroleum-based products, which contributes to carbon emissions.
- Recyclability: While PVC can be recycled, the process is not as straightforward as with other materials. It often gets downcycled into lower-quality products.
- Toxic Emissions: The production of PVC can result in the emission of harmful chemicals like chlorine gas.
- Longevity Factor: On the positive side, the longer lifespan of well-maintained PVC doors means less frequent replacement and, consequently, less resource consumption over time.
For a closer look at environmental issues related to PVC, visit the Environmental Impact of PVC Wikipedia page.
Sustainability of Aluminium
Aluminium offers some advantages and disadvantages from an environmental perspective as well.
- Recyclability: Aluminium is highly recyclable and can be recycled repeatedly without losing quality, making it relatively eco-friendly.
- Energy Intensive: However, the initial process of producing aluminium is energy-intensive, contributing to higher carbon emissions.
- Longevity: The long lifespan of aluminium doors means they need to be replaced less frequently, which is a point in favor of their sustainability.
- Eco-Friendly Coatings: Advances in technology allow for eco-friendly coatings that minimize environmental harm.
To learn more about the environmental aspects of aluminium, you can refer to the Environmental Impact of Aluminium Wikipedia page.

Installation and Maintenance
When choosing between PVC and Aluminium for doors, it’s not only the material’s properties you have to consider. Installation and maintenance are practical aspects that can significantly affect your experience and long-term satisfaction. Below we delve into the ease of installation and maintenance requirements for both materials.
Ease of Installation
Here’s what you need to know about installing PVC and Aluminium doors:
- PVC Installation: Typically, installing PVC doors is less complicated. The lighter weight of the material means that you usually don’t need specialized equipment for the installation. However, you might need an experienced contractor to ensure that the door is well-sealed and aligned.
- Aluminium Installation: Aluminium doors often require more expertise during installation because of their heavier weight and sometimes intricate designs. This may translate to higher labor costs.
For more about the general process of door installation, you can refer to the Door Wikipedia page.
Maintenance Requirements
Both PVC and Aluminium have specific maintenance needs:
- PVC Maintenance: PVC doors generally require less maintenance. A simple wash with soapy water can keep them looking new. However, over time, the color might fade, requiring either repainting or replacement.
- Aluminium Maintenance: Aluminium doors usually need a bit more upkeep. While they resist corrosion better than other metals, they may still corrode in highly acidic or salty environments. Special coatings can help maintain their appearance and durability.
For further insights into home maintenance, you might find the Home Repair Wikipedia page useful.
